Hi, I’m Chris Walton, author of this guide and CEO of Eton Venture Services.
I’ve spent much of my career working as a corporate transactional lawyer at Gunderson Dettmer, becoming an expert in tax law & venture financing. Since starting Eton, I’ve completed thousands of business valuations for companies of all sizes.

Read my full bio here.
In 2018, the collapse of UK construction giant Carillion sent shockwaves through the market.
Carillion had accumulated significant amounts of goodwill through years of acquisitions, but despite a weakened financial outlook management failed to report on goodwill impairment.
Because it’s recorded as an expense on the balance sheet, failing to record goodwill impairment gives a misleadingly positive view of earnings—as a result, Corillion was able to pay out £78m in dividends just two years before collapse.
Sudden liquidation and massive losses for investors followed.
For companies, this is a stark reminder: neglecting goodwill impairment testing can lead to financial write-downs that erode stakeholder trust.
If you’re carrying goodwill on your balance sheet, testing isn’t just a compliance checkbox, it’s key to maintaining financial transparency.
In this article, we guide you through the steps of goodwill impairment testing to help you avoid similar pitfalls.
Key Takeaways
|
Need a reliable goodwill valuations & impairment testing partner? Click here to learn about our goodwill impairment services. |
Both IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards) and U.S. GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles) provide guidelines for when and how to test for impairment.
Recent updates have streamlined the process, making it simpler and more cost-effective for companies to maintain transparency with their financial statements.
Under IFRS, companies are required to test goodwill for impairment at least annually or when a triggering event occurs that indicates the value may have dropped. We’ll cover these later in the article.
The testing is done at the cash-generating unit (CGU) level, which means testing the smallest part of the business that generates its own cash flow.
In November 2022, the IASB (International Accounting Standards Board) reaffirmed its decision to continue using the impairment-only model, which means companies do not gradually reduce the value of goodwill over time through amortization. Instead, they only test goodwill when there is a potential impairment, ensuring that goodwill stays on the balance sheet at its fair value.

The IASB also introduced updated disclosure requirements, encouraging companies to provide more detailed information about acquisitions.
The goal is to give investors better insights into how well the company’s acquisitions are performing and whether they are meeting the expected objectives

In the U.S., companies follow the guidelines set out in ASC 350 under U.S. GAAP. Similar to IFRS, U.S. GAAP requires companies to test goodwill for impairment annually and also when triggering events occur.
In this scenario, goodwill is tested at the reporting unit level. A reporting unit is typically a business unit or component of an operating segment with distinct financial information, regularly reviewed by management.
It’s important to note that the U.S. guidance, outlined in ASC 350, was simplified by ASU 2017-04, which removed the complex second step of the previous testing process.
Now, companies only need to compare the carrying value of the reporting unit to its fair value. If the carrying value exceeds the fair value, the difference is recorded as an impairment loss.
In the U.S., private companies have the option to amortize goodwill over 10 years or less and only perform impairment testing upon a triggering event. However, for public companies, the impairment-only model remains mandatory, requiring regular testing.

To avoid time pressure and ensure compliance with filing deadlines, companies should choose a testing date that allows plenty of time to complete the process before issuing financial statements.
While any date throughout the year can be selected, companies must use the same date each year.
Many public companies align their testing date with financial planning cycles, often choosing the first day or early in the fourth quarter. This timing enables them to use up-to-date financial data and complete the necessary steps without rushing to meet reporting requirements.
By following these guidelines, companies can reflect the true value of goodwill, avoid overstating assets, and ensure compliance with financial reporting standards.
As previously mentioned, companies must be vigilant about specific triggering events that necessitate an immediate reassessment of goodwill.
Notably, these triggering events can be both internal and external factors, highlighting the importance of monitoring the broader business environment as well as internal operations.
As Eric Croak, CFP, President at Croak Capital, emphasizes: “Too many people think of goodwill impairment as arising only when the company’s performance tanks. Really, goodwill impairment is just as likely to arise when the economy tanks, even if the company finds itself racking up record results.”
Here are some examples of triggers to pay attention to:
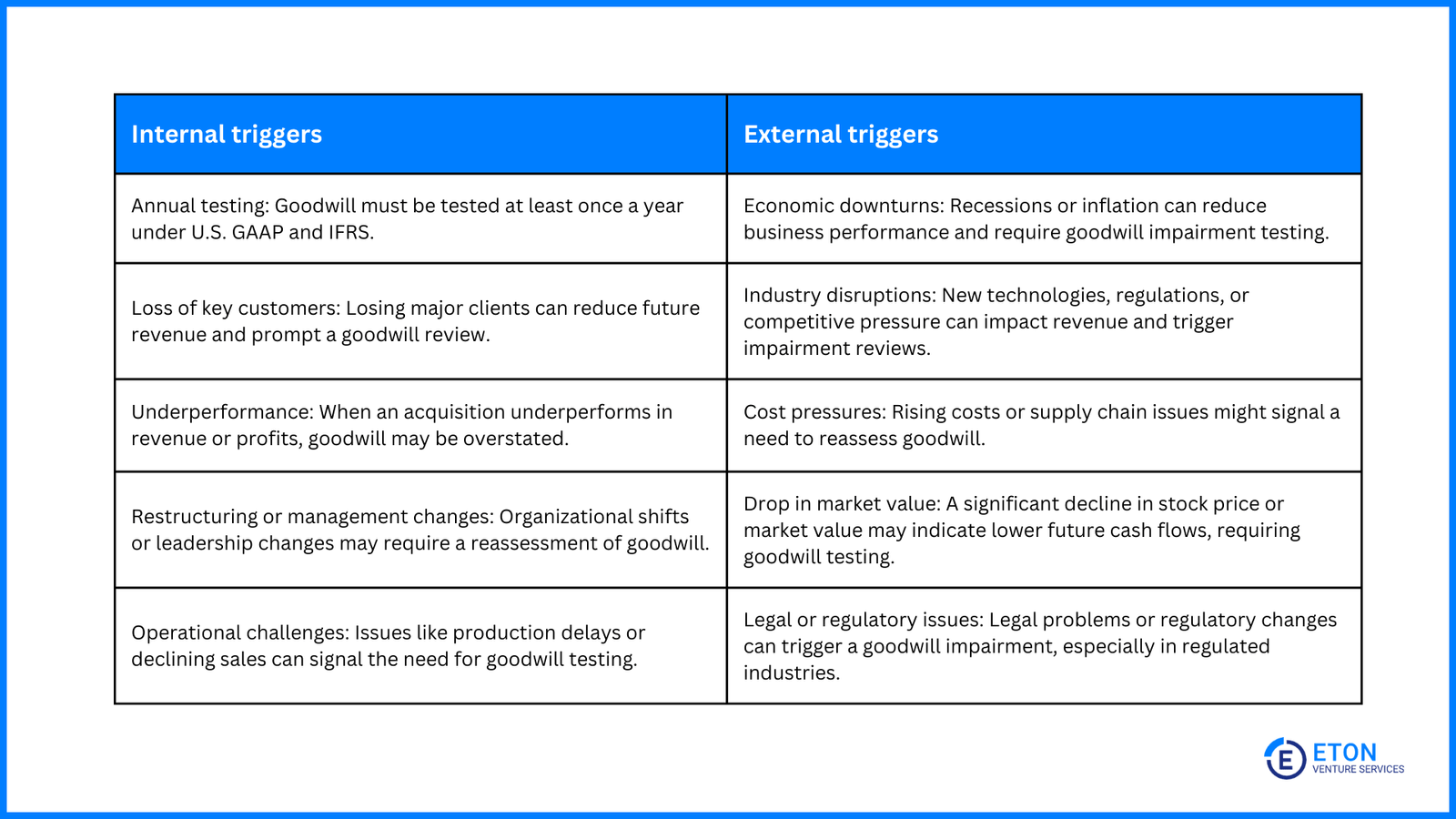
Find all 14 goodwill impairment-triggering events in this guide.
Now that we’ve covered the key triggering events that signal potential goodwill impairment, what happens next?
For many first-time acquirers, realizing that an acquisition’s value has dropped can be overwhelming. However, ignoring goodwill impairment can result in overstated profits and serious financial consequences down the line.
To avoid this, it’s necessary to follow a structured process for testing goodwill.
In this section, we’ll guide you step-by-step through the goodwill impairment testing process, ensuring you stay ahead of potential write-downs and maintain accurate financials.
U.S. GAAP offers the option of a qualitative assessment to determine whether further quantitative impairment testing is needed.
This assessment involves reviewing various internal and external factors, such as changes in market conditions, competitive pressures, and company-specific financial health.
If it’s deemed “more likely than not” that the fair value of a reporting unit is below its carrying amount, further quantitative testing is required.
However, if the likelihood is below 50%, the costly quantitative test can be skipped, allowing the company to conclude that goodwill is not impaired.
IFRS, however, mandates quantitative testing whenever there are indications of impairment, without the option for a qualitative assessment.
If goodwill impairment testing is required, the next step is to identify the units at which impairment will be assessed.
Depending on the applicable accounting standard, companies will either determine reporting units under ASC 350 or CGUs under IFRS.
Identifying these units sets the basis for evaluating the potential impairment of goodwill at the appropriate level.
If the qualitative assessment indicates impairment (under U.S. GAAP), or if there are impairment indicators under IFRS, the next step is to conduct a quantitative test to determine whether goodwill is impaired.
This step relies heavily on valuation methods to estimate the fair value of the reporting unit or CGU. While the common valuation methods include the income, market, and cost approaches, the main methods used in the goodwill impairment testing process are the income and market approaches:
Using these valuation methods together or individually helps ensure that fair value estimates are comprehensive and realistic. When selecting the appropriate methods, consider the following:
After conducting the quantitative test, it is important to ensure that the fair value estimates are robust and not overly reliant on any single set of assumptions.
Sensitivity analysis serves this purpose by varying key assumptions, such as discount rates, growth projections, and market conditions, to gauge their impact on the fair value of the reporting units or CGUs.
By assessing multiple scenarios, from optimistic to pessimistic, companies can understand the potential variability in the fair value estimates and the associated risks.
This proactive assessment not only strengthens the reliability of the impairment test but also supports internal decision-making and provides stakeholders with insight into the company’s risk management practices.
After estimating fair value, compare it to the carrying value of each reporting unit or CGU.
Under U.S. GAAP, the carrying value is compared to the estimated fair value of the reporting unit. Under IFRS, the carrying value is compared to the recoverable amount (the higher of fair value less costs of disposal or value in use).
If the carrying value exceeds the fair value or recoverable amount, it indicates potential goodwill impairment.
If impairment is indicated, the next step is to measure the impairment loss.
Under amended U.S. GAAP, this is now a simplified process: the impairment loss is the difference between the carrying value of the reporting unit and its fair value.
Under IFRS, the impairment loss is the difference between the carrying amount of the CGU and its recoverable amount.
The impairment loss is then recorded as an operating expense on the income statement and reduces the carrying value of goodwill on the balance sheet.
It’s important to note here that once goodwill is impaired, the loss cannot be reversed under both standards.
After recognizing and measuring the impairment loss, the details must be disclosed accurately in the financial statements. The disclosure should include the amount of the impairment, the reporting unit or CGU affected, and the rationale behind the impairment.
Companies must also outline the methods and key assumptions used in estimating the fair value, providing transparency on any changes from previous estimates.
This detailed disclosure, typically found in the financial statement footnotes, is vital for maintaining stakeholder trust, ensuring compliance with accounting standards, and allowing investors and creditors to fully understand the company’s financial position and the factors affecting it.
To simplify the goodwill impairment testing process, let’s look at an example involving Company A, which acquired Company B for $10 million.
At the time of acquisition, Company B had identifiable net assets valued at $7 million, resulting in $3 million of goodwill recorded on Company A’s balance sheet.
A year later, due to an economic downturn, Company A faces declining revenue from the business segment that includes Company B, triggering an impairment test for goodwill.
First, Company A identifies the reporting unit (under U.S. GAAP) or CGU (under IFRS) for impairment testing, which in this case is Company B.
The company then proceeds with a quantitative test, estimating the fair value of Company B using valuation methods such as the Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) model and market multiples.
After completing these valuations, Company A estimates the fair value of Company B to be $6 million.
Since the carrying value of Company B (net assets plus goodwill) is $10 million and exceeds the estimated fair value of $6 million, an impairment loss is indicated.
Under U.S. GAAP, the impairment loss is the difference between the carrying value of the reporting unit ($10 million) and its fair value ($6 million), resulting in a $4 million impairment loss.
Under IFRS, the impairment loss is similarly calculated as the difference between the carrying amount of the CGU ($10 million) and its recoverable amount ($6 million), leading to a $4 million impairment loss.
In both cases, the $4 million impairment loss is recorded as an operating expense, and the carrying value of goodwill on the balance sheet is reduced.
To complete the goodwill impairment testing process effectively, it’s crucial to not only follow each step methodically but also to ensure that the entire process is well-documented.
Proper documentation supports transparency, enables an effective audit trail, and helps justify the estimates and judgments made during the impairment testing process.
Here are some practical tips to help ensure your documentation is complete and compliant:
Record review and sign-off: Identify who conducted and reviewed the testing process, and ensure sign-off by relevant management.
To effectively test goodwill for impairment, there are several best practices to keep in mind:
Goodwill impairment testing can be tricky, with many steps and details to get right. It’s more than just a box to check for compliance – it’s about making sure your business is valued correctly to avoid financial problems later on.
With complex tasks like identifying triggers and performing valuations, having expert support makes a big difference.
Working with professionals ensures the impairment test is done thoroughly and follows the latest rules. This not only reduces the risk of mistakes but also reassures investors and stakeholders that your financials are accurate.
By getting expert help, you protect your business and make sure its true value is accurately reflected in your financial statements.
Under IFRS, goodwill is tested at the cash-generating unit (CGU) level, while US GAAP tests at the reporting unit level. IFRS requires impairment testing annually or when triggers occur, while US GAAP offers an optional qualitative assessment first.
Yes, under US GAAP, companies can first perform a qualitative assessment. If it’s unlikely that the reporting unit’s fair value is below its carrying value, a quantitative test isn’t required. IFRS, however, does not allow this option.
The main valuation methods used in goodwill impairment testing are the income approach (using discounted cash flows) and the market approach (comparing similar companies).
Common triggers include economic downturns, loss of key customers, underperformance, market disruptions, and significant changes in management or business strategy. Any of these events may indicate the need to test goodwill for impairment.
Companies must disclose the amount of the impairment, the impacted unit, and the reasons behind the impairment. They should also explain the valuation methods and key assumptions used, ensuring transparency in their financial statements.
Schedule a free consultation meeting to discuss your valuation needs.
Chris Walton, JD, is is President and CEO and co-founded Eton Venture Services in 2010 to provide mission-critical valuations to private companies. He leads a team that collaborates closely with each client’s leadership, board of directors, internal / external counsel, and independent auditors to develop detailed financial models and create accurate, audit-ready valuations.